vishal@solitaire-overseas.com
Stud Type Supplier
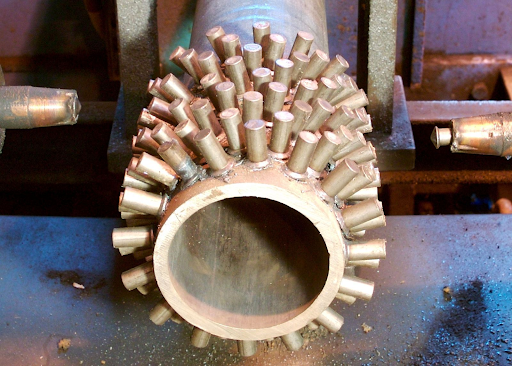
Studded Tubes are specialized metal tubes with welded studs arranged along their length. This unique design enhances the tube’s surface area, making them ideal for applications that require high heat transfer efficiency, such as in boilers and refineries where they are commonly used for reheating processes.
- Space-Efficient: Compact design allows for more efficient use of space.
- Durability: Built for long-lasting performance under demanding conditions.
- Effective Heat Transfer: Preferred over finned tubes for enhanced heat transfer applications.
- High Performance: Studded tubes optimize heating processes with their increased surface area.
| Base Tube O.D | Base Tube Thickness (mm) | Fin Height | Tube Length (Mtr) |
| (mm) | (mm) | ||
| 38 mm ~219 mm | 4.0 mm ~20 mm | 6.0 mm ~ 38 mm | ≤ 15Mtrs |
| Base Tube Material | Fin Material | ||
| Carbon Steel ,Alloy Steel ,Stainless Steel | Carbon Steel ,Alloy Steel , | ||
| Tube O.D.: | 25~355.6 (mm) | 1”~14”(NPS) |
| Tube Wall Thk.: | 3.5~28.6 (mm) | 0.14”~1.1” |
| Tube Length: | ≤25,000 (mm) | ≤82 ft |
| Stud Dia.: | 6~25.4 (mm) | 0.23”~1” |
| Stud Height: | 10~50.8 (mm) | 0.4”~2” |
| Stud Pitch: | 8~30 (mm) | 0.3”~1.2” |
| Stud Shape: | Cylindrical, Elliptical, Round, Lens type | |
| Stud to tube surface angle: | Vertical, angular, staggered rows | |
| Stud Material: | C.S. (most common grade is Q235B) S.S. (most common grade are AISI 304, 316, 409, 410, 321,347 ) A.S. | |
| Tube Material: | C.S. (most common grade is A106 Gr.B) S.S. (most common grade are TP304, 316, 321, 347 ) A.S.(most common grade are T/P5,9,11,22,91 ) | |
| * This table is used as a general guide to our capabilities, please call us for any other customized cases. | ||
|
Technical Range |
||
|
Tube OD(mm) |
Tube Thickness(mm) |
Tube Height(mm) |
|
60-219 |
4-20 |
10-38 |
|
Material & Length Range |
||
|
Tube |
Stud |
Tube Length(m) |
|
A106GrB, A335 P5/P9 A204 TP304 |
CS ANSI 410, SS304 5%Cr-1/2Mo |
1-15 |

| Boilers and Furnaces: In boilers and water tube furnaces, studded tubes facilitate efficient heating. They are commonly used in water tube boilers where studded, oval-shaped tubes are welded to improve water heating. |
| Petrochemical Industries: High-density crude oil flows through studded tubes, where heat is applied externally to convert the oil into liquid form. This liquid is then sent for further processing. |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency: The surface area of a studded tube offers enhanced heat transfer capabilities, reducing the need for numerous bare pipes. Just one studded tube can often replace the surface area of 4 to 10 bare pipes, making them a compact solution in heat-intensive applications. |
| Corrosive Environments: In industries handling harsh fuels, studded tubes offer protection against corrosion. Applying a protective coating on the external surfaces shields them from environmental damage, extending their durability. |
| Soda Ash Boilers and Fluidized Bed Reactors: Studded tubes are ideal in environments where erosion is common. Their design minimizes wear, making them effective in applications like soda ash boilers and fluidized bed reactors. |
| Steel Plants and Power Plants: With applications in air coolers, heat exchangers, and other high-heat setups, studded tubes are valuable in steel and power plants for their reliable heat conduction and compact design. |
| Studded tubes combine durability, space efficiency, and enhanced heat transfer, making them indispensable across multiple industrial sectors. |
 FAQ
FAQ
Studded tubes are metal tubes with studs welded along their length in a specific pattern. This design increases surface area, enhancing heat transfer, and is commonly used in boilers and refineries for reheating applications.
There are several types of studs, including threaded studs, shear connectors, unthreaded studs, studs with internal threads, boiler tube studs, and heat- and scale-resistant welding studs, typically ranging from 3-25 mm in diameter and produced from various materials.
A fully threaded stud is a threaded bar used with nuts at each end. A double-end stud has threads at both ends and an unthreaded middle section for precise alignment.

